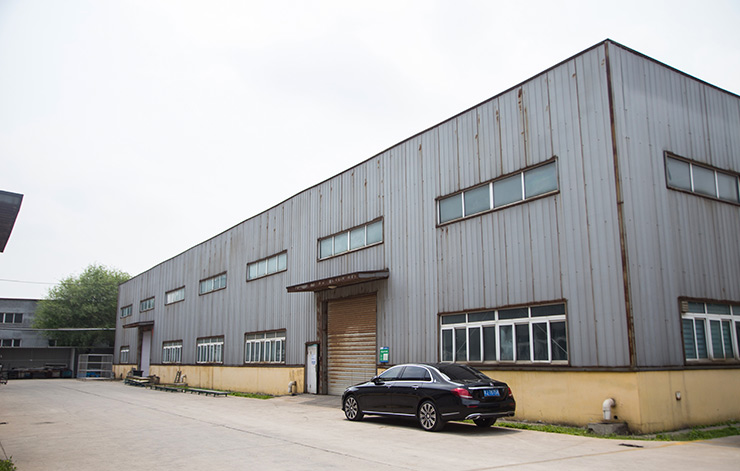
Aluminum die castings
Aluminum die castings
Aluminum die casting is a kind of pressure casting parts, which uses a pressure casting mechanical die-casting machine equipped with a casting mold to pour the aluminum or aluminum alloy heated to liquid into the feeding port of the die-casting machine, and then cast the aluminum parts or aluminum alloy parts with the limited shape and size of the mold by the die-casting machine. Such parts are usually called aluminum die castings.
Aluminum die castings have different names in different places, such as aluminum die castings, aluminum die castings, aluminum die castings, aluminum alloy die castings, etc.
Because the l aluminum and aluminum alloy have good fluidity and plasticity, and the casting process is cast in the pressure die-casting machine, the aluminum die-casting can make a variety of more complex shapes, and can also make higher precision and finish, so as to greatly reduce the mechanical processing of castings and the casting allowance of l aluminum or aluminum alloy, which not only saves power, l materials, but also greatly saves labor costs; Aluminum and aluminum alloys have excellent thermal conductivity, small specific gravity and high machinability; Therefore, aluminum die castings are widely used in automobile manufacturing, internal combustion engine production, motorcycle manufacturing, motor manufacturing, oil pump manufacturing, transmission machinery manufacturing, precision instruments, landscaping, power construction, architectural decoration and other industries.
classification
Aluminum die castings can be manufactured into aluminum die-casting auto parts, aluminum die-casting auto engine pipe fittings, aluminum die-casting engine cylinders, aluminum die-casting gasoline engine cylinder heads, aluminum die-casting valve rocker arms, aluminum die-casting valve supports, aluminum die-casting power accessories, aluminum die-casting motor end covers, aluminum die-casting housings, aluminum die-casting pump housings, aluminum die-casting building accessories, aluminum die-casting decorative accessories, aluminum die-casting guardrail accessories, aluminum die-casting aluminum wheels and other parts.
Stainless steel balls are widely used in the surface treatment of non-ferrous l die castings, castings, aluminum profiles, auto parts, machinery manufacturing, hardware, pump and valve industries. It mainly focuses on removing the oxide skin on the product surface, burrs on the edge surface, surface roughening, matte fruit, leveling and strengthening, and rust removal. Stainless steel shot, commonly known as stainless steel wire cut shot, is refined by wire drawing, cutting, rounding and other processes. Its appearance is bright, rust free and round (cut shot, cylindrical). Stainless steel shot has moderate hardness, pure ingredients and large coverage. Because it does not have the shortcomings of general cast steel shot, such as pores and abnormal shapes, its service life is longer. The performance of this product can completely replace imported products, and the price is significantly lower than imported products, saving costs for customers. The surface of castings treated with stainless steel shot is bright and clean without rust, and there is no need for post-treatment such as pickling, which is conducive to environmental protection. You can choose two different shapes of products: pre polished round and non pre polished shot.
technological process
The four basic processes in die-casting aluminum industry are annealing, normalizing, quenching and tempering, which are called "four fires" in die-casting. In the process of die-casting, quenching and tempering are closely related, and both are indispensable.
It is understood that annealing is to heat the workpiece. When it is heated to the appropriate temperature, the die casting is cooled slowly according to the different materials selected, so that the internal structure of the l is close to equilibrium. Normalizing is to heat the workpiece to a suitable temperature and then cool it in the air. It is mainly used to improve the cutting function of materials, and it can also be used to end die-casting for some parts that need less. Quenching is to heat and keep the workpiece warm, and then quickly cool it in water or other quenching media such as inorganic salt solution. After this process, the steel parts produced will become hard and brittle at the same time. In order to reduce the brittleness of steel parts, quenched steel parts can be placed at a temperature below 650 ℃ higher than the normal temperature for a long time, and then cooled, which is called tempering.
The application of aluminum die castings aluminum materials and aluminum alloys have good fluidity and plasticity, so various die castings with complex shapes and great difficulties can be made. The castings cast with aluminum alloys and l aluminum have high precision and surface finish, which greatly reduces the mechanical processing volume of castings, greatly reduces the labor intensity, and saves electricity and l materials at the same time. Because of its high internal and external quality, aluminum die castings are widely used in automobile manufacturing, internal combustion engine production, motorcycle manufacturing, motor manufacturing, transmission machinery manufacturing, precision instruments, landscaping, power construction, and other industries, and become the new favorite of the die casting industry.


























 Tianjin public network security12022302000634
Tianjin public network security12022302000634


